What is dow theory?
Nse live scanner Dow Theory
Dow Theory
Charles Dow & Edward
Jones established Dow Jones & Company in 1882.Charles Dow &
Edward Jones They created the two indices i.e., the Dow Jones Industrial
Average (DJIA) and the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) to provide a
good indication of the health of the Economides explored the relationship
between the two indices and published his theories in editorials in the Wall
Street Journal, which pioneered Technical Analysis. Even in today’s highly
technologically developed market, Dow Theory holds its basic tents’ Dow’s death
in 1902, William Hamilton continued his work of writing editorials until 1929.Robert
Rhea then collected the work of both of these men and used it as a basis to
publish The Dow Theory in 1932.
Dow theories six
basic tenets:
1. The average
discounts everything:
The market reflects all available
information which can affect it positively or negatively. What it cannot
anticipate is happening of the natural calamities, even that are discounted as
soon as it happens. It is similar to that of the first pillar of the technical
analysis; the prices of the stocks absorb all the news as soon as the
information is released. Prices show the sum total of all the hopes, fears and
expectations of all participants. Interest rate movements, earnings
expectations, revenue projections, presidential elections, product initiatives
and all else are already priced into the market.
2. The Market has
three trends:
According to Dow theory, the market has only three trends
A. Primary trend:
In Dow theory, primary trend is also considered as major trend in the market.
It has a long-term impact and may remain in effect for more than 1 year. It may
also influence the secondary and minor trend. Dow looks at it as tides in the
sea as it affects the overall impact dramatically.
B. Secondary trend:
Dow call a correction in the primary trend as secondary trend. It usually last
for three weeks to three months. It generally retraces 33% to 66% of the
primary trend. In a bullish market secondary trend will be a downward movement
and in a bearish market it will be a rally. Dow calls it as waves in the sea.
C. Minor trend:
The “short swing” or minor movement varies with opinions from hours to a month
or more.
3.The three trends
may be simultaneous.
For instance, a daily minor trend in a bearish secondary
trend in a bullish primary trend.
The Market trends
have three phases:
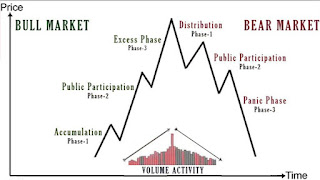
Accumulation phase: It is a period when investors are actively buying
stock against the general opinion of the market. At this phase trader keeps
buying and selling the stock but the prices do not change as the demand is far
less the supply in the market.
Absorption phase: In the second phase investor starts accumulating
stock. All the technical indicator starts working as there is a huge
participation in the market. This phase continues until rampant speculation
occurs.
Distribution phase: After a huge hype in the prices because of the
skewed supply of the stock the prices begins to retrace as the astute investors
begin to distribute their holdings to the market. As a result of it the prices
start falling along with the volume.
4. Average must
confirm each other:
In Dow’s time, the two averages
were the Industrials and the Rails. The logic behind the theory is simple:
Industrial companies manufactured the goods and the rails shipped them. When
one average recorded a new secondary or intermediate high, the other average
was required to do the same in order for the signal to be considered valid.If the two averages acted in
harmony, with both reaching new highs or lows around the same time period, then
the prices of each was said to be confirming.
When one of these averages climbs
to an intermediate high, then the other is expected to follow suit within a
reasonable amount of time. If not, then the averages show “divergence” and the
market is liable to reverse course.In other words, if one average
went to a new high, while the other was left behind, then there was bearish
divergence. If the opposite occurred, with one average reaching a new low while
the other held above a previous bottom, then the divergence was bullish.
5. Volume must confirm the trend:
Dow recognized the volume as a
secondary but important factor in confirming price signals. In other words,
volume should increase in the direction of the major trend. In a major uptrend
volume should
increase with the rally in price
and should diminish during correction. Also, in a major downtrend volume should
expand with the fall in prices and should contract during upward ripples.
6. A trend is assumed to be in effect until it gives a definite signal
of reversal:
Dow was a firm believer that
market remains in a trend. It may deviate for a while because of noise but it
will return as soon as its effect is over. It is like Newton’s law of motion
“an object in motion tends to continue in motion, until some external force
causes it to change direction”.
There are many trend reversal
signals like support/resistances, price patterns, trend lines, moving averages.
Some indicators can also provide warnings of loss of momentum.





No comments